Atlantic Niño is the Atlantic counterpart of El Niño in the Pacific, often referred to as El Niño's little brother. It was previously thought to have only regional influence on rainfall variability in West Africa, but a growing number of studies have shown that Atlantic Niño also plays an important role in the development of... Continue Reading →
On the fate of the 2023-24 El Niño
As of July 2023, the developing El Niño in the Pacific has already exceeded its sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies of 1°C in Niño3.4 region (central Pacific) and 3°C in Niño1+2 region (far eastern Pacific). This is the first time to have those SST thresholds exceeded since the development of 1997-98 "supper El Niño" in... Continue Reading →
El Niño’s little brother in the Atlantic may not be so little when it comes to its impact on hurricanes
Atlantic Niño, characterized by warm sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies in the eastern equatorial Atlantic, is the Atlantic counterpart of the Pacific El Niño. Due to its smaller size in zonal extent, it is often referred to as El Niño’s little brother. It was previously thought to have a limited regional influence on rainfall variability... Continue Reading →
Java-Sumatra Niño/Niña: two long-lost siblings of El Niño
There are many siblings, cousins, and distant relatives of El Niño spanning the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans who share a feature in common: ocean surface temperature anomalies along eastern boundaries linked to changes in the upwelling of cooler water from below. So far, climate scientists have identified a total of 14 members of this... Continue Reading →
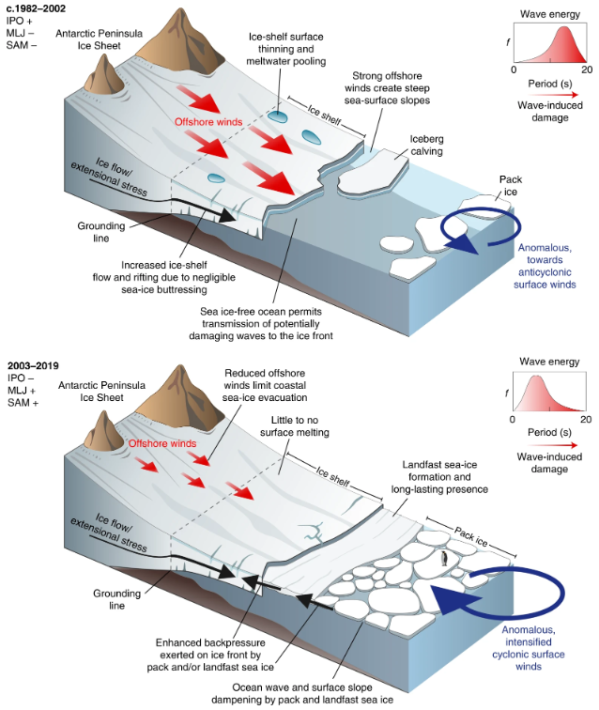
Nearshore sea ice shield Antarctic ice shelves from the damaging impact of ocean waves
The Larsen ice shelves extend along the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula over the northwest part of the Weddell Sea. From north to south, these segments are called the Larsen A, B, C, and D, bordered by Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf south of the Weddell Sea. In 1995, the Larsen A ice shelf completely disintegrated,... Continue Reading →
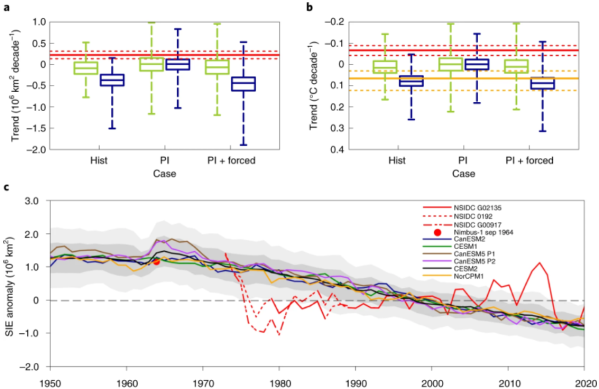
Why climate models are unable to reproduce the observed Antarctic sea-ice expansion
Antarctic sea-ice has expanded over the period of continuous satellite monitoring, which seemingly contradicts ongoing global warming resulting from increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases. A variety of hypotheses have been proposed to explain the observed Antarctic sea-ice expansion and corresponding model–observation discrepancy, but the issue remains unresolved. In a new study published in Nature Climate... Continue Reading →
Future El Niño events will develop faster and persist longer
Previous studies based on the climate models participating in the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP) have suggested an increase in the frequency of extreme El Niño events in the 21st Century in response to increasing greenhouse gases. Several studies have attributed these shifts in El Niño frequency and amplitude to the projected changes in the... Continue Reading →
ENSO plays little role in early-season Atlantic hurricane activity
This is a guest blog by Robert West. Robert is a postdoctoral research associate in the Northern Gulf Institute (NGI) at the Mississippi State University and is also affiliated with NOAA's Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. Differences in sea surface temperature anomalies (SSTAs) between the tropical Atlantic and Pacific oceans are known to influence atmospheric... Continue Reading →
A Seasonal Probabilistic Outlook for Tornadoes (SPOTter) in the Contiguous U.S.
This new study accepted in Monthly Weather Review (Lee et al., 2021) presents an experimental model for Seasonal Probabilistic Outlook for Tornadoes (SPOTter) in the contiguous U.S. for March, April and May, and evaluates its forecast skill. This forecast model uses the leading empirical orthogonal function modes of regional variability in tornadic environmental parameters (i.e.,... Continue Reading →
What caused the abrupt reduction of the South Indian Ocean heat & sea level in 2014–2016 and the ensuing quick recovery?
A decade-long increase of the basin-wide sea level and heat content in the subtropical southern Indian Ocean (SIO) during 2004–2013 ended abruptly, immediately following the onset of the strong 2014–2016 El Niño. Interestingly, this unprecedented drop of the SIO heat quickly recovered during the weak 2017–2018 La Niña. A study recently published in Science Advances... Continue Reading →